General Dermatology
Medical Dermatology
Medical Dermatology is the diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions. Some of the practice’s most commonly treated skin conditions are: Acne, Contact Dermatitis, Cysts, Eczema, Fungal Infection, Hair Loss, Hives, Melasma, Nail Disease, Pre-Cancers (Actinic Keratosis), Psoriasis, Rosacea, Scabies, Skin Cancer, Skin Tags, Warts, and Wrinkles. We welcome all ages and ethnicities.
Surgical Dermatology
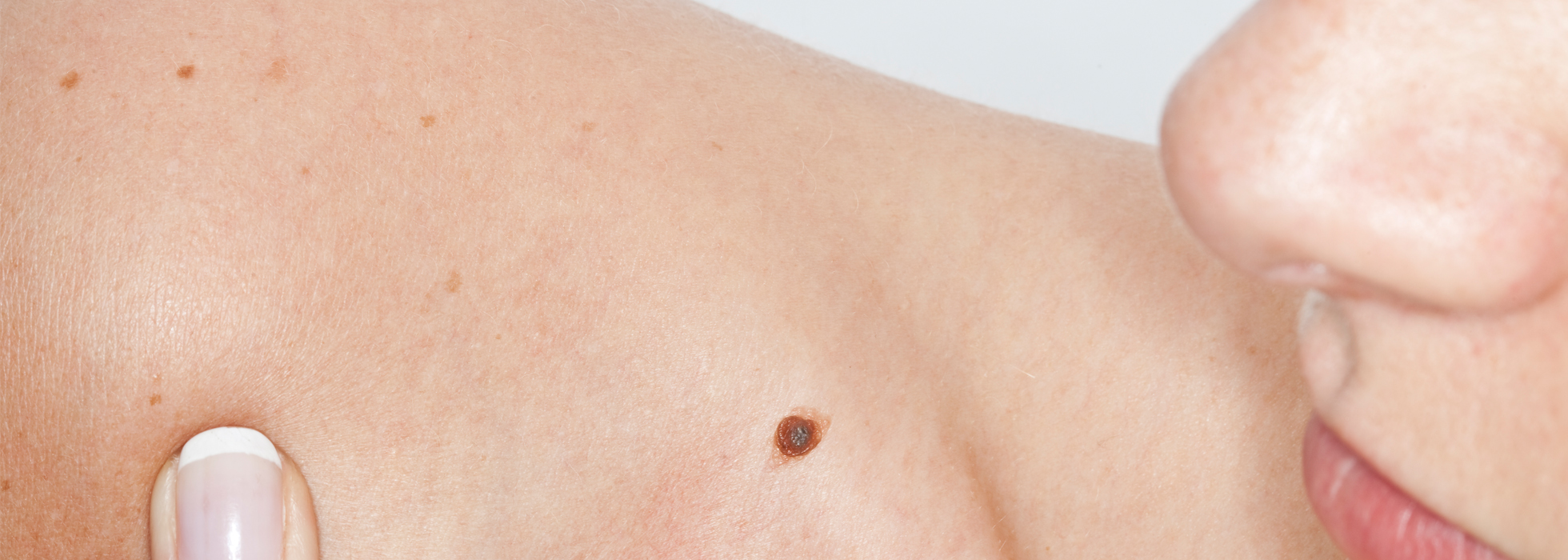
Surgical Dermatology addresses abnormal moles, cysts, other growths and skin cancers that may require surgical removal. We encourage our patients to do a full body check every month for any skin changes. Make sure you routinely schedule a visit for a complete skin examination.
Skin Cancer Treatment
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. If detected early, it can be easily treated and cured.
Skin Cancer Prevention and Treatment:
Most skin cancers develop on the visible outer layer of the skin (the epidermis), particularly on sun-exposed areas like the face, head, hands, arms, and legs. In addition to sun exposure, family history may also play a role. Diagnosing skin cancer usually requires a skin biopsy, where a small piece of skin is removed for examination under a microscope. If skin cancer is detected before it has spread to surrounding tissues, chances of a complete cure are excellent.
Most Common Types of Skin Cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (also called BCC) comes from the basal cells in the lowest part of the epidermis. About 80-85% of skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (also called SCC) comes from the skin cells (keratinocytes) that make up the top layers of the skin. About 10% of skin cancers are SCC. Skin cancer may often be preceded by lesions called pre-cancers. The most well-known of these lesions is called actinic keratosis, an early stage of SCC.
Melanoma comes from skin cells called melanocytes, which create pigment called melanin that gives skin its color. Just 5% of all skin cancers are melanoma. Although less common, melanomas are a very dangerous type of skin cancer and are the leading cause of death from skin cancer.
Signs & Symptoms:
- A sore that comes and goes but never completely heals
- A shiny bump or nodule, especially if it appears pearly or translucent (these can look brown or reddish and resemble a mole)
- A slightly raised pink growth with a crusted depression in the center, possibly with tiny blood vessels (capillaries) visible on the surface
- A patch of skin that is red or irritated, especially on the chest, shoulders, or limbs
- A white or yellowish waxy scar with poorly defined borders
Prevention:
The best protection against skin cancer is to minimize sun exposure and use a broad spectrum sunscreen. Avoid tanning beds. Cover yourself with sun-protective clothing. Examine your skin from head to toe once every month. Make sure you routinely schedule a visit for a complete skin examination.
Treatment:
Several factors determine treatment of skin cancer, including the type, size, extent, location and number of lesions, as well as your medical and family history of skin cancers. Treatment options include: medications, curettage (scraping) and electrodesiccation (burning), cryotherapy, excision or Mohs Surgery. Radiation and chemotherapy may also be recommended.